- Published on
Enabling ECS Events with Terraform
- Authors

- Name
- James Brown

Svix is the enterprise ready webhooks sending service. With Svix, you can build a secure, reliable, and scalable webhook platform in minutes. Looking to send, receive, and transform webhooks? Give Svix a try!
In October, Amazon Web Services announced a new user-friendly feature to display and query event history for Elastic Container Service in the console. Unfortunately, there isn't an API to configure this functionality, so it's not supported by by Infrastructure-as-Code systems like Terraform1. This blog post is a quick tutorial on how to set up ECS Event Capture using Terraform and some elbow grease.
At its core, ECS Event Capture is three things:
- A CloudWatch log group with the name
/aws/events/ecs/containerinsights/${ecs_cluster_name}/performance - A CloudWatch event rule with a that looks like
EventsToLogs-abcedf-3wfJqgRwkYjHX84MmFFsbKSwrX5LBwPSVcNcwqevGYn6and an appropriate filter - A CloudWatch event target pointing from the event rule to the log group
The only tricky part here is the CloudWatch event rule; it turns out that the frontend looks for that name specifically, and it's not clear a priori what would be generating that 33-character alphanumeric hash at the end of the string. Thankfully, Amazon ships helpers.tsx un-minified in the AWS console, so we can just look at the source!
export async function hashFromString(message: string): Promise<string> {
const hash = await crypto.subtle.digest('SHA-256', new TextEncoder().encode(message))
const encodedHash = base58.encode(new Uint8Array(hash))
return encodedHash
}
export async function getEventBridgeRuleName(
clusterName: string,
clusterArn: string
): Promise<string | undefined> {
const hash = await hashFromString(`"${clusterArn}"`)
const clusterPrefix = clusterName.substring(0, 6)
return `EventsToLogs-${clusterPrefix}-${hash}`
}
Base58, hm? I've never used it, but it's the same idea as base64, just with some ambiguous characters removed. There's no function to do it in Terraform directly, but it only took me a few minutes to knock together a prototype provider that implements what we need2.
Let's put that provider together with some Terraform code and go to town; the code below is a full implementation of this feature, structured as a Terraform module:
locals {
truncated_name = substr(var.ecs_cluster_name, 0, 6)
# note the extra quotes
hash = provider::base58::base58sha256("\"${var.ecs_cluster_arn}\"")
}
variable "ecs_cluster_name" {
type = string
nullable = false
}
variable "ecs_cluster_arn" {
type = string
nullable = false
}
variable "retention_in_days" {
type = number
default = 14
}
data "aws_caller_identity" "current" {}
terraform {
required_version = ">= 1.0"
required_providers {
base58 = {
source = "svix-jbrown/base58"
version = "~> 0.0.2"
}
}
}
# This must exactly match the name that the console creates
resource "aws_cloudwatch_log_group" "this" {
name = "/aws/events/ecs/containerinsights/${var.ecs_cluster_name}/performance"
retention_in_days = var.retention_in_days
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule" "console" {
name = "EventsToLogs-${local.truncated_name}-${local.hash}"
event_pattern = jsonencode({
"source" : ["aws.ecs"],
"detail" : {
"clusterArn" : [var.ecs_cluster_arn]
}
})
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_target" "performance" {
target_id = "performance"
rule = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.console.name
arn = aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this.arn
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "this" {
statement {
sid = "EventBridgeToCloudWatchLogs"
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["events.amazonaws.com", "delivery.logs.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogStream"
]
resources = [
aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this.arn,
"${aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this.arn}:*",
]
condition {
test = "StringEquals"
variable = "aws:SourceAccount"
values = [data.aws_caller_identity.current.account_id]
}
condition {
test = "ArnEquals"
variable = "aws:SourceArn"
values = [aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.console.arn]
}
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"logs:PutLogEvents"
]
resources = [
"${aws_cloudwatch_log_group.this.arn}:*:*"
]
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["events.amazonaws.com", "delivery.logs.amazonaws.com"]
}
condition {
test = "ArnEquals"
variable = "aws:SourceArn"
values = [aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.console.arn]
}
}
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_log_resource_policy" "this" {
policy_document = data.aws_iam_policy_document.this.json
policy_name = "ecs_events_${var.ecs_cluster_name}"
}
With that, your ECS cluster will show Event capture as enabled:

And if you switch over to the "Event history" tab, you'll be able to see container event history for this cluster:
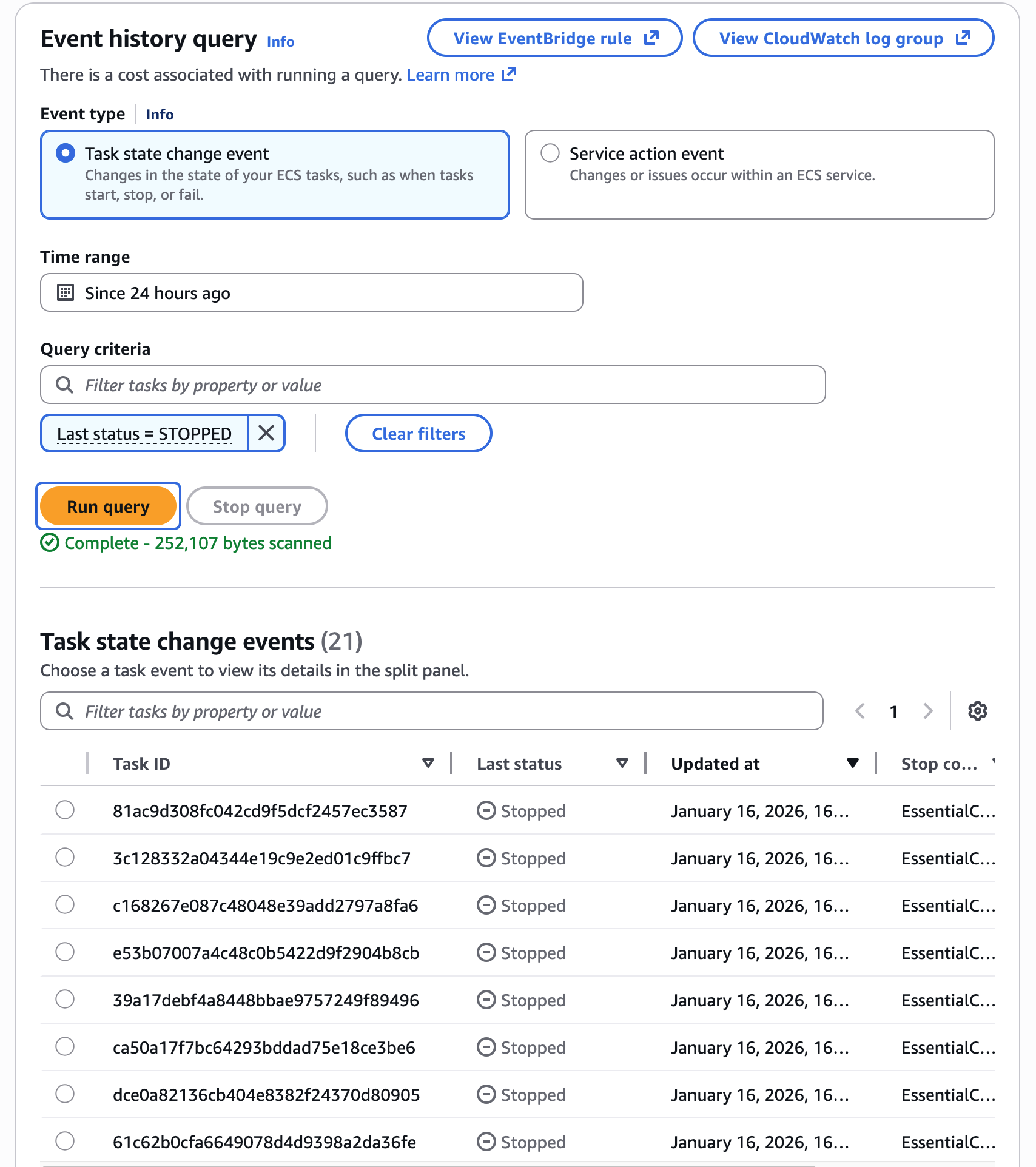
Not too bad for a few minutes work! Hopefully this will be helpful for someone else out there. If that's you, and you're passionate about improving developer experience and love designing and operating big web-scale systems, come work with us!
As always, stay tuned at https://www.svix.com/blog to hear more about what we're working on, and be sure to follow us on Github or RSS for the latest updates for the Svix webhook service, or join the discussion on our community Slack.
Footnotes
See Issue 44653 on the
terraform-provider-awsrepository. ↩The Terraform docs on building a provider turn out to be pretty great! Even though I haven't written Go in a couple of years and have never made a Terraform provider before, this entire project took something like 25 minutes, including reading the documentation and figuring out how to get a contemporary version of GnuPG to generate an RSA private key, since Terraform Registry doesn't accept ECC keys (it's just
gpg --full-generate-keyto get the same interactive menu that you might be used to from the last, oh, 25 years). ↩